Neurology diagnoses and treats disorders of the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, as well as thought and memory.
Overview and definition
Neurology is the medical specialty focused on the diagnosis and treatment of disorders affecting the nervous system. This complex system includes the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, which control all body functions, from movement and sensation to thought and memory. A neurologist is a medical doctor who specializes in these disorders and treats a wide range of conditions that can impact a person’s quality of life.
Common Conditions Treated in Neurology

Neurologists manage a vast array of conditions, including:
- Stroke (Ischemic and Hemorrhagic)
- Epilepsy and seizure disorders
- Movement disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease and tremor
- Neurodegenerative diseases, like Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias
What is a Neurologist?

A neurologist is a specialist who diagnoses and manages conditions of the nervous system. They do not perform surgery (i.e., neurosurgery), but they are experts in the complex pathways of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. They are trained to identify the location and cause of a problem within the nervous system and to develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
The Central and Peripheral Nervous System
The nervous system is divided into two main parts:
- The Central Nervous System (CNS): This is the body’s main processing center, consisting of the brain and spinal cord.
- The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): This consists of all the nerves outside of the CNS. It connects the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body, including the limbs and organs, and transmits signals back and forth.

Symptoms and Causes
Neurological symptoms are diverse and depend entirely on which part of the nervous system is affected. Because the nervous system controls everything, a symptom can range from a muscle twitch to a major personality change.
Common Warning Signs of a Neurological Disorder
Symptoms often relate to a loss of function. You should consult a doctor if you experience:
- Suddenly, severe headache
- Loss of strength or weakness in a limb or one side of the face
- Numbness, tingling, or loss of sensation
- Dizziness, vertigo, or problems with balance
- Seizures (convulsions)
- Problems with memory, speech, or confusion
- Tremor, slowness of movement, or involuntary movements
- Sudden vision problems (blurriness, double vision, or loss of vision)
Causes of Neurological Conditions
The causes of neurological disorders are broad and can include:
- Vascular: Problems with blood supply, such as stroke.
- Genetic: Inherited conditions, such as Huntington’s disease or muscular dystrophy.
- Degenerative: The progressive breakdown of nerve cells, as in Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s.
- Autoimmune: The body’s immune system attacks its own nerves, such as in Multiple Sclerosis.
- Infectious: Caused by viruses, bacteria, or other organisms (e.g., meningitis).
- Traumatic: Injury to the brain or spinal cord.
30
Years of
Excellence
Trusted Worldwide
With patients from across the globe, we bring over three decades of medical expertise and hospitality to every individual who walks through our doors.Book a Free Certified Online
Doctor Consultation
[elementor-template id=”207591″] Table of Contents
[elementor-template id=”211216″]
Diagnosis and Staging
A precise neurological diagnosis begins with a thorough clinical exam to test reflexes, muscle strength, sensation, and cognitive function. This exam is the cornerstone for localizing the problem. To confirm a diagnosis and determine its severity, neurologists use advanced tools. Neuroimaging, such as MRI and CT scans, provides detailed pictures of the brain and spinal cord. Electrical tests, like an EEG for seizures or an EMG for nerve issues, measure nervous system activity. In some cases, a lumbar puncture is needed to analyze cerebrospinal fluid. This comprehensive data allows the team to “stage” the condition, such as classifying the progression of a neurodegenerative disease. MEETING WITH THE DOCTORThe Neurological Examination
This is the most important diagnostic tool in neurology. The neurologist will systematically test specific functions, including:
- Mental status (cognition, memory, speech)
- Cranial nerves (vision, hearing, facial movement)
- Motor system (strength, tone, coordination)
- Sensory system (touch, pain, vibration)
- Reflexes
Neuroimaging and Electrical Tests
To see the structure and function of the nervous system, several tests are used:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and CT Scan: These imaging tests create detailed pictures of the brain and spinal cord to find tumors, strokes, or structural damage from MS.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): This test records the electrical activity of the brain. It is essential for diagnosing epilepsy.
- Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV): These tests measure electrical activity in muscles and nerves. They are used to diagnose peripheral nerve damage, myasthenia gravis, and ALS.
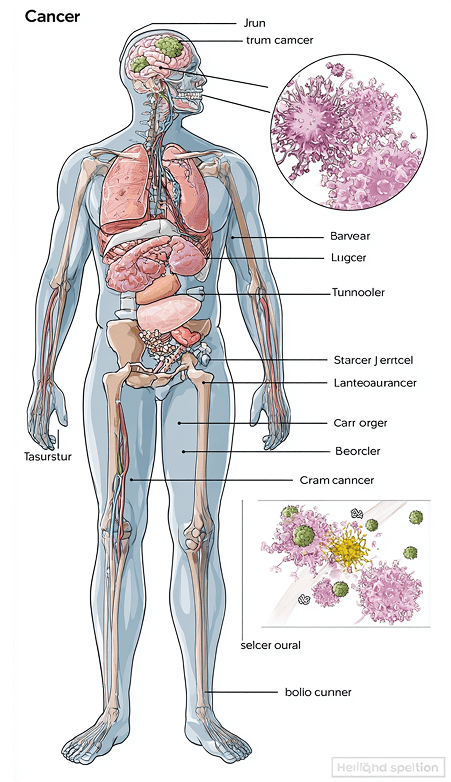
Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap)
In this procedure, a small sample of cerebrospinal fluid (the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord) is collected. This fluid is analyzed to detect signs of infection (meningitis), inflammation (Multiple Sclerosis), or certain types of bleeding in the brain.
Treatment Details
Neurological treatment is highly specific to the underlying condition, aiming to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and restore function. For many disorders, medication management is the primary approach. In acute events like stroke, emergency interventional treatments (thrombectomy) are time-critical. For movement disorders or epilepsy, advanced options like Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) may be considered. A comprehensive plan also integrates physical, occupational, and speech therapy to maximize quality of life and independence.
Medical Management and Pharmacotherapy
Medications are the foundation of treatment for many neurological conditions. This includes:
- Anti-epileptic drugs to prevent seizures.
- Disease-modifying therapies to slow the progression of Multiple Sclerosis.
- Medications to manage the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
- Thrombolysis (“clot-busting” drugs) for acute ischemic stroke.
Preventive and abortive medications for migraines.
Interventional and Surgical Therapies
While many conditions are managed medically, some require interventions:
- Acute Stroke Intervention: This includes mechanical thrombectomy, a procedure to physically remove a large blood clot from a brain artery.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): An implanted device sends electrical signals to brain areas that control movement, used to treat Parkinson’s disease, tremor, and dystonia.
- Neurosurgery: Required for removing brain tumors, clipping aneurysms, or for some epilepsy cases.
The Medical Center
The complexity of the nervous system demands a center with deep expertise and advanced diagnostic tools. At Liv Hospital, our neurology department collaborates closely with neurosurgeons, neuroradiologists, and physical therapists. This integrated, multidisciplinary team ensures a comprehensive evaluation for every patient. Our facility is equipped with state-of-the-art neuroimaging and electrodiagnostic technology (EEG, EMG), enabling precise diagnoses and the delivery of sophisticated treatments, from acute stroke care to long-term management of chronic conditions.
Our Multidisciplinary Neurology Team

No neurological condition is treated in isolation. Our neurologists lead a “Brain Team” that includes neurosurgeons, interventional neuroradiologists, and specialized rehabilitation therapists. This team meets to discuss complex cases, such as stroke or brain tumors, ensuring that every patient benefits from a 360-degree care plan that is tailored to their specific needs.
Advanced Neuro-Diagnostic Technology
Accurate diagnosis depends on superior technology. Our center is equipped with high-field 3T MRI scanners for high-resolution images of the brain and spine. We also have dedicated neurophysiology labs for advanced EEG monitoring (including video-EEG for epilepsy) and comprehensive EMG/NCV testing, enabling our specialists to obtain the most precise data possible.
Specialized Clinics and Acute Stroke Care
We provide focused care through specialized clinics for conditions like Epilepsy, Multiple Sclerosis, and Movement Disorders. Furthermore, our hospital operates a 24/7 acute stroke response protocol. Our stroke team is always ready to perform rapid evaluation and life-saving interventional treatments, such as thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy, to minimize brain damage and maximize recovery.
Book a Free Certified Online
Doctor Consultation
[elementor-template id=”207591″] 
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What are the common side effects of chemotherapy?I am item content. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
How can I manage my diet during treatment?I am item content. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
What is immunotherapy and is it right for me?I am item content. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
How long will my recovery take after surgery?I am item content. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
What support services are available for patients and families?I am item content. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

RELATED VIDEOS
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XHOmBV4js_EUnderstanding Your Cancer Diagnosis: A Beginner’s Guide
This video breaks down the basics of a cancer diagnosis, explaining common terms, what to expect, and questions to ask your doctor. A gentle introduction for newly diagnosed patients.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XHOmBV4js_ENavigating Treatment Side Effects: Tips for Comfort
Learn practical strategies and expert advice on managing common side effects like fatigue, nausea, and pain during cancer treatment. Find ways to improve your daily comfort and well-being.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XHOmBV4js_ELife Beyond Cancer: Thriving in Survivorship
Explore the journey of cancer survivorship, focusing on emotional recovery, long-term health, and embracing a fulfilling life after treatment. Hear inspiring stories and expert insights.
[elementor-template id=”211456″][elementor-template id=”186412″]Neurology is the medical specialty focused on the diagnosis and treatment of disorders affecting the nervous system. This complex system includes the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, which control all body functions, from movement and sensation to thought and memory. A neurologist is a medical doctor who specializes in these disorders and treats a wide range of conditions that can impact a person’s quality of life.
The Central and Peripheral Nervous System
The nervous system is divided into two main parts:
- The Central Nervous System (CNS): This is the body’s main processing center, consisting of the brain and spinal cord.
- The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): This consists of all the nerves outside of the CNS. It connects the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body, including the limbs and organs, and transmits signals back and forth.
What is a Neurologist?
A neurologist is a specialist who diagnoses and manages conditions of the nervous system. They do not perform surgery (i.e., neurosurgery), but they are experts in the complex pathways of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. They are trained to identify the location and cause of a problem within the nervous system and to develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
Common Conditions Treated in Neurology
Neurologists manage a vast array of conditions, including:
- Stroke (Ischemic and Hemorrhagic)
- Epilepsy and seizure disorders
- Movement disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease and tremor
- Neurodegenerative diseases, like Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and other demyelinating diseases
- Headaches and migraines
- Neuromuscular disorders, such as ALS (Lou Gehrig’s disease)
- Infections of the nervous system (e.g., meningitis)
Symptoms and Causes
Neurological symptoms are diverse and depend entirely on which part of the nervous system is affected. Because the nervous system controls everything, a symptom can range from a muscle twitch to a major personality change.
Common Warning Signs of a Neurological Disorder
Symptoms often relate to a loss of function. You should consult a doctor if you experience:
- Suddenly, severe headache
- Loss of strength or weakness in a limb or one side of the face
- Numbness, tingling, or loss of sensation
- Dizziness, vertigo, or problems with balance
- Seizures (convulsions)
- Problems with memory, speech, or confusion
- Tremor, slowness of movement, or involuntary movements
- Sudden vision problems (blurriness, double vision, or loss of vision)
Causes of Neurological Conditions
The causes of neurological disorders are broad and can include:
- Vascular: Problems with blood supply, such as stroke.
- Genetic: Inherited conditions, such as Huntington’s disease or muscular dystrophy.
- Degenerative: The progressive breakdown of nerve cells, as in Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s.
- Autoimmune: The body’s immune system attacks its own nerves, such as in Multiple Sclerosis.
- Infectious: Caused by viruses, bacteria, or other organisms (e.g., meningitis).
- Traumatic: Injury to the brain or spinal cord.
Diagnosis and Staging
A precise neurological diagnosis begins with a thorough clinical exam to test reflexes, muscle strength, sensation, and cognitive function. This exam is the cornerstone for localizing the problem. To confirm a diagnosis and determine its severity, neurologists use advanced tools. Neuroimaging, such as MRI and CT scans, provides detailed pictures of the brain and spinal cord. Electrical tests, like an EEG for seizures or an EMG for nerve issues, measure nervous system activity. In some cases, a lumbar puncture is needed to analyze cerebrospinal fluid. This comprehensive data allows the team to “stage” the condition, such as classifying the progression of a neurodegenerative disease.
The Neurological Examination
This is the most important diagnostic tool in neurology. The neurologist will systematically test specific functions, including:
- Mental status (cognition, memory, speech)
- Cranial nerves (vision, hearing, facial movement)
- Motor system (strength, tone, coordination)
- Sensory system (touch, pain, vibration)
- Reflexes
Neuroimaging and Electrical Tests
To see the structure and function of the nervous system, several tests are used:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and CT Scan: These imaging tests create detailed pictures of the brain and spinal cord to find tumors, strokes, or structural damage from MS.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): This test records the electrical activity of the brain. It is essential for diagnosing epilepsy.
- Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV): These tests measure electrical activity in muscles and nerves. They are used to diagnose peripheral nerve damage, myasthenia gravis, and ALS.
Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap)
In this procedure, a small sample of cerebrospinal fluid (the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord) is collected. This fluid is analyzed to detect signs of infection (meningitis), inflammation (Multiple Sclerosis), or certain types of bleeding in the brain.
Treatment Details
Neurological treatment is highly specific to the underlying condition, aiming to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and restore function. For many disorders, medication management is the primary approach. In acute events like stroke, emergency interventional treatments (thrombectomy) are time-critical. For movement disorders or epilepsy, advanced options like Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) may be considered. A comprehensive plan also integrates physical, occupational, and speech therapy to maximize quality of life and independence.
Medical Management and Pharmacotherapy
Medications are the foundation of treatment for many neurological conditions. This includes:
- Anti-epileptic drugs to prevent seizures.
- Disease-modifying therapies to slow the progression of Multiple Sclerosis.
- Medications to manage the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
- Thrombolysis (“clot-busting” drugs) for acute ischemic stroke.
- Preventive and abortive medications for migraines.
Interventional and Surgical Therapies
While many conditions are managed medically, some require interventions:
- Acute Stroke Intervention: This includes mechanical thrombectomy, a procedure to physically remove a large blood clot from a brain artery.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): An implanted device sends electrical signals to brain areas that control movement, used to treat Parkinson’s disease, tremor, and dystonia.
- Neurosurgery: Required for removing brain tumors, clipping aneurysms, or for some epilepsy cases.
Neurological Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is critical for recovery and adaptation.
- Physical Therapy: Helps to improve strength, mobility, and balance.
- Occupational Therapy: Focuses on adapting to daily life activities, such as dressing and cooking.
- Speech Therapy: Addresses problems with speaking, swallowing, and cognitive communication.
The Medical Center
The complexity of the nervous system demands a center with deep expertise and advanced diagnostic tools. At Liv Hospital, our neurology department collaborates closely with neurosurgeons, neuroradiologists, and physical therapists. This integrated, multidisciplinary team ensures a comprehensive evaluation for every patient. Our facility is equipped with state-of-the-art neuroimaging and electrodiagnostic technology (EEG, EMG), enabling precise diagnoses and the delivery of sophisticated treatments, from acute stroke care to long-term management of chronic conditions.
Our Multidisciplinary Neurology Team
No neurological condition is treated in isolation. Our neurologists lead a “Brain Team” that includes neurosurgeons, interventional neuroradiologists, and specialized rehabilitation therapists. This team meets to discuss complex cases, such as stroke or brain tumors, ensuring that every patient benefits from a 360-degree care plan that is tailored to their specific needs.
Advanced Neuro-Diagnostic Technology
Accurate diagnosis depends on superior technology. Our center is equipped with high-field 3T MRI scanners for high-resolution images of the brain and spine. We also have dedicated neurophysiology labs for advanced EEG monitoring (including video-EEG for epilepsy) and comprehensive EMG/NCV testing, enabling our specialists to obtain the most precise data possible.
Specialized Clinics and Acute Stroke Care
We provide focused care through specialized clinics for conditions like Epilepsy, Multiple Sclerosis, and Movement Disorders. Furthermore, our hospital operates a 24/7 acute stroke response protocol. Our stroke team is always ready to perform rapid evaluation and life-saving interventional treatments, such as thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy, to minimize brain damage and maximize recovery.